The following repeaters are available:
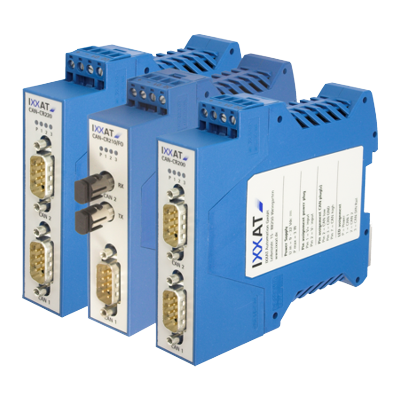
CAN Repeaters
CAN repeaters for copper cable connetcion
Fiber optic CAN Repeaters
Fiber optic repeaters for areas with high electromagnetic disturbances
Introduction
Repeaters are used to establish a physical coupling of two or more segments of a CAN bus system. They can be used to implement tree or star topologies as well as for long drop lines. In addition, network segments can be electrically decoupled using a galvanically isolated repeater.
Advantages
The lines coupled by the repeater are independent electric segments that can be optimally terminated in terms of signals. In this way topologies can be implemented that are not possible with a pure line of the bus due to electrical reflections.
According to the transceiver output capacities, the division of a CAN bus system into several subsystems, connected via CAN Bus Repeaters, increases the maximum number of bus nodes.
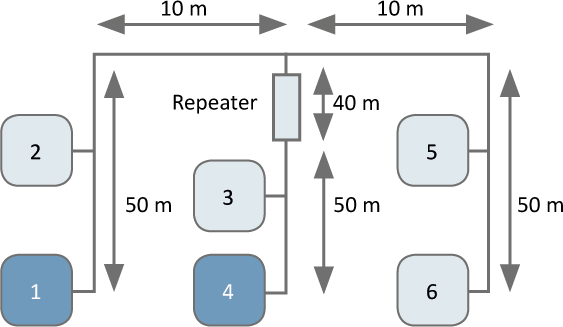
Another application of repeaters is the coupling of different physical CAN layers by means of high/low-speed repeaters, optical repeaters, or optical star couplers.
Bus-timing
As signaling is not directed in CAN, the repeater logic has to translate the signals of the segment received into the other and has to ensure that the input signals are not back-coupled. In terms of signals, the repeater corresponds to a line with relevant delay time. Therefore, it cannot be used to extend a CAN bus system.
Using repeaters does not influence the real-time behavior of a system because in terms of transmission behavior it corresponds to a network that consists only of lines.