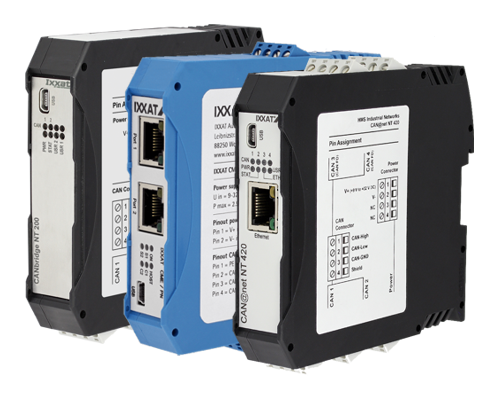
The following bridges/gateways are available:
CAN-to-CAN Bridges
Easy connection of CAN systems enabling system expansion and message filtering
CAN-to-X Bridges
Connection of CAN systems using Bluetooth or Ethernet
Introduction
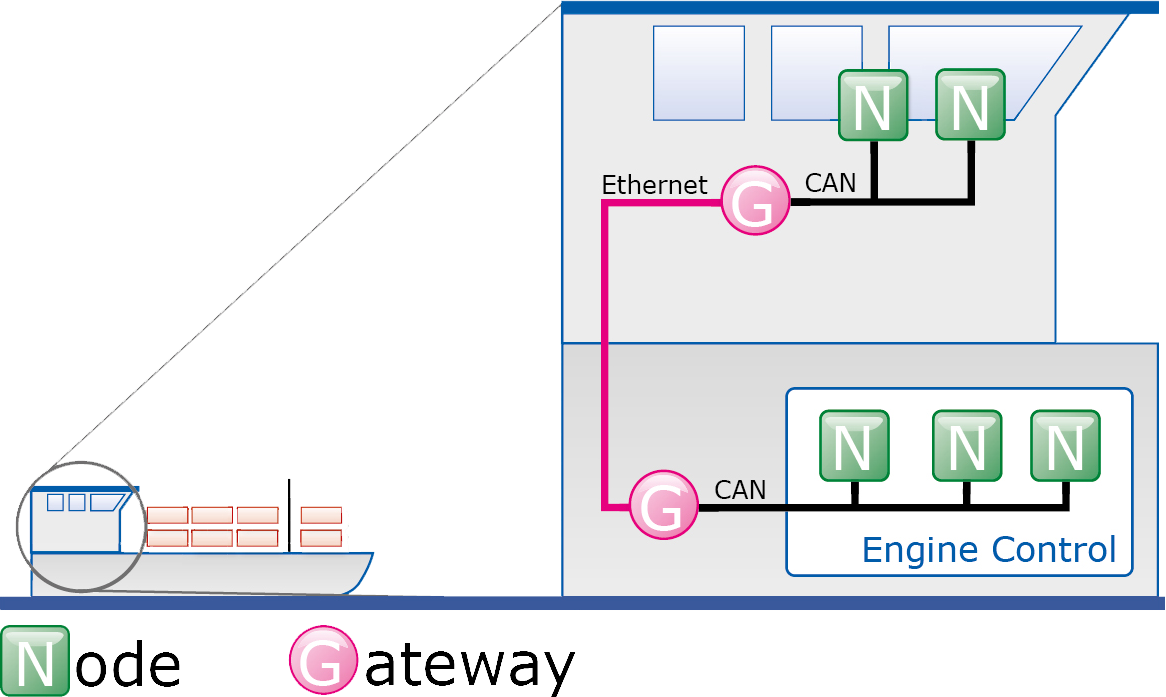
CAN bridges and CAN gateways are infrastructure components with which complex network structures can be implemented. A CAN bridge can connect CAN networks of different bit rates or protocols with each other. It is based on the store-(modify)-forward principle where CAN messages are received by a sub-network and then transmitted to the other sub-network.
Translation and filter rules can also be used, allowing a protocol adaptation to be carried out between the sub-networks. A bridge can also provide simple gateway functions.
Bridges
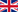
Unlike the CAN bus repeater, the CAN Bridge enables the enlargement of the maximum network size so that the sub-systems are fully self-sufficient with regard to bus arbitration. Independent of each other in terms of their real-time behavior, CAN bus sub-networks connected by bridges are to be regarded as independent networks.
CAN bus bridges are appropriate for creating hierarchical networks by transferring only the information to the connected sub-networks via bridges which are relevant to the sub-network. The bridge function can also be executed with the aid of other transmission systems. For example, the 'CAN-Ethernet-CAN'-bridge is connected via two Ethernet-TCP/IP gateways which enable connection to remote CAN networks.
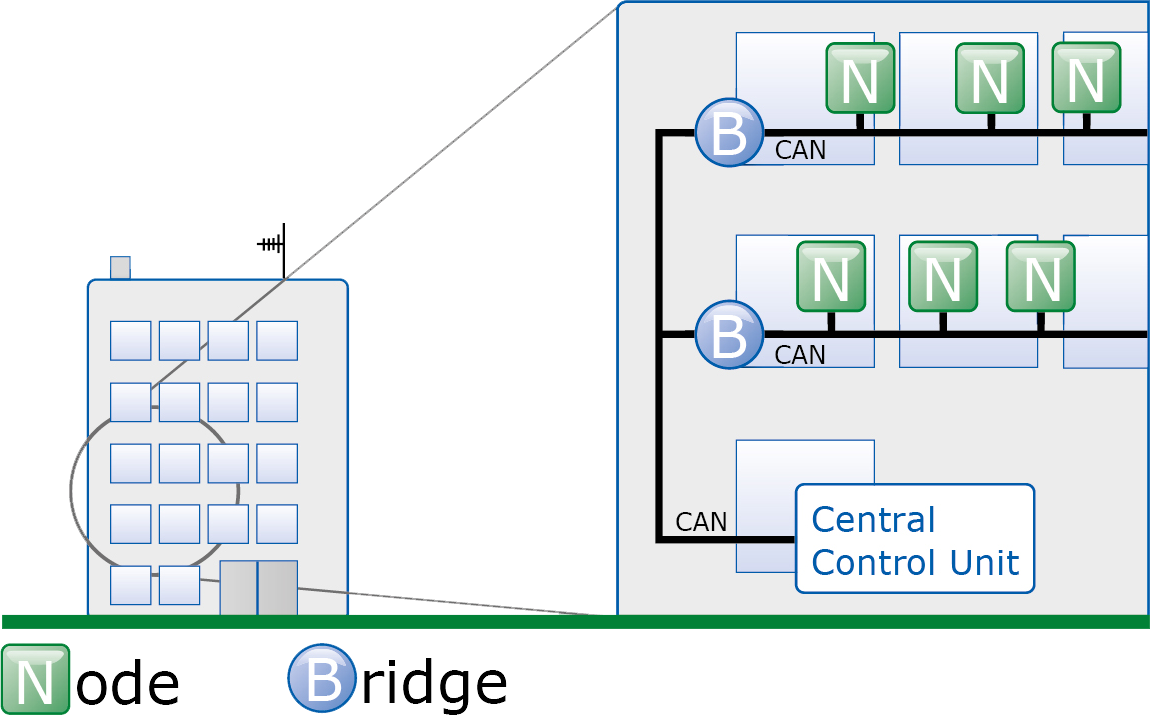
Gateways
As an extension to the CAN bridges, CAN gateways allow for access to CAN networks via other communication systems. In each case, the protocols of the connected bus systems are mapped to the other communication model.
CAN Bridge
Using the CANbridge, CAN systems within a building can be separated for every flor, due to this the maximum system expansion can be easily extended.