OPC UA & MQTT Support
Connect to IoT-software with OPC UA or MQTT
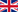
Anybus CompactCom 40 Ethernet products are available in a special version that is able to communicate with IoT protocols such as OPC UA and MQTT. This means that industrial Ethernet protocol data (for example PROFINET or EtherNet/IP) is processed as usual by the CompactCom — and data from the device can also be sent to an IT system via OPC UA or MQTT.
With OPC UA or MQTT communication on the factory floor, it is possible to use a computer, server or edge gateway to relay information to IT systems and clouds. Anybus CompactCom enables devices and machines on the factory floor to communicate with any industrial network using OPC UA or MQTT.
Possebilities
- Tap data from the host device, all ADI data is readable (application parameters)
- Provide on-the-fly statistics from your device
- Predictive maintenance — Spot problems before they occur
- Collect data to perform data analysis (local server or on IT level)
Features and benefits
- Support for micro-embedded profile
- Supports Discovery Services
- User name and password authentication
- Supports DataChange Subscription
- Timestamp supported via discovery server or time protocol of the industrial network
- OPC UA extension to all standard Anybus features
- Available for PROFINET and EtherNet/IP
How it works
The application will enable the OPC UA functionality where the ADIs (application parameters) are readable as variable nodes through OPC UA.
The modelled device is of type CompactCom40DeviceType which is a subtype of the OPC UA DeviceType.
It is possible for the application to change certain parameters e.g. the name of the device and its device type, to make the application manufacturer specific.
About OPC UA
OPC Unified Architecture (UA) is a service-oriented industrial communication standard for secure and reliable data exchange.
OPC UA is platform-independent and ensures a seamless flow of information among devices from multiple vendors. It defines services for data exchange between clients and servers including access to real-time data, monitoring of alarms and events, access to historical data and other applications.
The standard is managed by the OPC Foundation.
Anybus CompactCom OPC UA functionality
- Support for micro-embedded profile
- Supports Discovery Services
- User name and password authentication
- Supports DataChange Subscription
- Timestamp supported via discovery server or time protocol of the industrial network
- OPC UA extension to all standard
About MQTT
MQTT (Message Queue Telemetry Transport) is a publish/subscribe messaging protocol ideal for IT/OT bridging and IIoT solutions. Based on its light-weight and straight forward approach, it has become one of the most popular protocols enabling industrial data and information exchange.
MQTT is based around a message broker (server) to which industrial devices (clients) connect. The clients exchange information via the broker based on topics with a flexible syntax. The broker uses the topics to decide which clients to receive a message.
Compared to OPC UA, MQTT is more flexible and easier to implement. On the other hand, it lacks the data, service models and security schemes provided by OPC UA.
Anybus CompactCom MQTT functionality
- MQTT client acting as publisher
- MQTT version 3.1.1
- Json data encoding with Time stamp
- Transparent transfer supported
- Last Will and QoS 0-2 supported
- User name and password authentication
- Maximum 4K data from host application (maximum 8K on network including Json encoding).
IT-functionality
Every Anybus CompactCom for Industrial Ethernet comes, in addition to the industrial protocol, with numerous IT functions as standard
- FTP Server
- E-mail Client
- File Manager
- TCP/IP Sockets
- Web Server
- JSON
- Server Side Include (SSI)
CompactCom provides direct access to the TCP/IP stack socket interface, enabling custom protocols to be implemented over TCP/UDP.
The built-in web server provides a flexible environment for end-user interaction and configuration purposes. The powerful combination of JSON, SSI, and client-side scripting allows access to objects and file system data, enabling the creation of ad-vanced graphical user interfaces.